


Next: 7. SUMMARY AND FINAL
Up: A Detection Method for
Previous: 5.3 KBOs research using
6. THE VALIDITY OF THE DETECTION
The main limitation of this method is the uniqueness of the occultation.
It is not
possible to redo an observation to verify the reality of the detection.
Moreover, the objects detectable with this method are mostly
undetectable by other techniques. Then the question is: How can we be sure
we have
detected an occultation by a KBO and not an asteroid, a comet, or a bird or an
electric discharge?
This question has already been encountered during studies of planetary rings.
The Uranus and the Neptune ring system, undetectable from the ground until
recently, have been discovered and explored by stellar occultations. The
reality of an occultation by the Uranus rings have been confirmed by the
symmetrical dips observed on the two sides of the planet. But the incomplete
arcs of Neptune have been much more difficult to catch. To assess the reality
of an arc detection, the observations were conducted on 2 nearby telescopes.
Some occultations provided arc profiles with S/N ratio good enough to fit the
dip with a semitransparent bar model and reject the hypothesis of a solid body
[Sicardy, Roques and Brahic 1991].
During planetary occultations, isolated events were often observed with one
telescope but with S/N not good enough to fit them [Nicholson et al. 1990].
One of them has been confirmed by simultaneous detection with nearby
telescopes during an occultation by Uranus. It has been analyzed as the
occultation by a 1.4 km object near Uranus [Sicardy et al. 1986]. Using the
present work, we found that the probability of occultation by KBOs during such
observations was some tens of percent per night. Then, several isolated events
observed during the planetary occultations could be due to KBOs.
Different methods can be used to asses the reality of the occultation and to
possibly discriminate an occultation from a false event or an occultation by
another object
in the Solar System:
- As for planetary occultations, the reality of an occultation can be
confirmed by simultaneous observation from nearby telescopes, or
with multi-object photometers. However, this
does not allow us to determine the distance of the occulting object.
- The direction of the shadow motion can also be used, as done by the TAOS
team who validate the event by successive detections by telescopes
spaced a few kilometers apart on an east-west baseline.
- Table IV shows the parameters of the occultations in terms of the distance
of the occulting object.
The minimum size of detectable objects (last column) shows that
asteroids of a few
tens of meters could be detected. However, the asteroid
population is probably
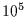 times less numerous than the KBO population.
Then, even if smaller objects are involved, the probability of
occultation by KBOs is a thousand times larger than by asteroids.
times less numerous than the KBO population.
Then, even if smaller objects are involved, the probability of
occultation by KBOs is a thousand times larger than by asteroids.
The velocity of a KBO in the sky plane for a given direction depends
on the distance of the occulting object (Eq.5).
The probability of occultation is minimal and the duration of the occultation is
maximal toward the quadrature, that is 81
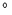 from the opposition for
objects at 40 AU from the Sun. But the direction of the quadrature changes
with the distance of the occulting objects: When several events are detected,
the number of events with respect to the direction of observation
from the opposition for
objects at 40 AU from the Sun. But the direction of the quadrature changes
with the distance of the occulting objects: When several events are detected,
the number of events with respect to the direction of observation 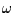 can
be used to infer the distance of the population of occulting objects. The high
occultation rates estimated above for large telescopes
make these speculations plausible.
can
be used to infer the distance of the population of occulting objects. The high
occultation rates estimated above for large telescopes
make these speculations plausible.
- If an occultation is observed at different wavelengths, the profiles are
different (see Fig.5) and the comparison of the dip profiles could give
information on the Fresnel scale and, then, on the distance of the occulting
object.
Figure 5:
Synthesized lightcurve of the occultation of a star by a
0.2 km KBO observed at 0.4 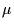 m (upper curve) and 1.2
m (upper curve) and 1.2  m
(lower curve). The star radius projected at 40 AU is 0.3 km and the noise
m
(lower curve). The star radius projected at 40 AU is 0.3 km and the noise
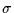 =1%.
=1%.
 |
- An occultation profile on a unique lightcurve with a high S/N and high
speed acquisition should exhibits the diffraction fringes (see Fig.6
and [Roques 1999]).
These features may be analyzed to retrieve the Fresnel scale
and thus provide the distance of the occulting object (this analysis,
as the previous point, are not in
the scope of the present paper and will be done elsewhere).
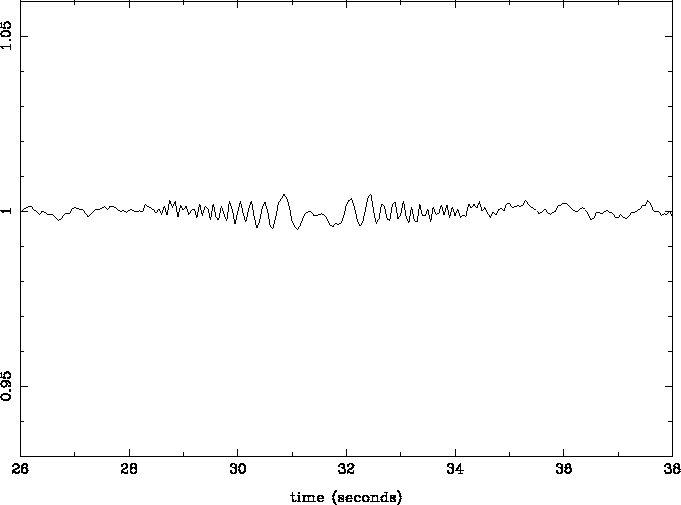
Figure 6:
Synthesized lightcurve of a stellar occultation
observed with high photometric precision 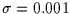 and exhibiting diffraction fringes. The object radius is 40m and
the star radius is 100m, both projected at 40 AU. The acquisition
frequency is 20Hz and the object apparent velocity is 3km/s.
and exhibiting diffraction fringes. The object radius is 40m and
the star radius is 100m, both projected at 40 AU. The acquisition
frequency is 20Hz and the object apparent velocity is 3km/s.
 |



Next: 7. SUMMARY AND FINAL
Up: A Detection Method for
Previous: 5.3 KBOs research using
DESPA, Observatoire de Paris
2000-04-05
![]() from the opposition for
objects at 40 AU from the Sun. But the direction of the quadrature changes
with the distance of the occulting objects: When several events are detected,
the number of events with respect to the direction of observation
from the opposition for
objects at 40 AU from the Sun. But the direction of the quadrature changes
with the distance of the occulting objects: When several events are detected,
the number of events with respect to the direction of observation ![]() can
be used to infer the distance of the population of occulting objects. The high
occultation rates estimated above for large telescopes
make these speculations plausible.
can
be used to infer the distance of the population of occulting objects. The high
occultation rates estimated above for large telescopes
make these speculations plausible.

