The geometry of a tilted dipole field is shown in Figure
A1. The centrifugal equator is defined as the locus
of the most distant points from the spin axis along magnetic field lines.
The centrifugal equator is plotted here in the Jovian meridian plane which
contains the magnetic moment ![]() of a centered dipole, tilted
by
of a centered dipole, tilted
by ![]() with respect to the Jupiter spin axis
with respect to the Jupiter spin axis ![]() .
The angle
.
The angle ![]() between the magnetic and centrifugal equator is maximum
in this
between the magnetic and centrifugal equator is maximum
in this
![]() plane and is about
plane and is about ![]() for
small
for
small ![]() [ Hill et al., 1974] (for Jupiter
[ Hill et al., 1974] (for Jupiter ![]()
![]() ). A given
point P of the magnetosphere is defined by
two coordinates: (i) the dipole equatorial radius L of its own magnetic field line and
(ii) its centrifugal latitude, that is the angle between OP and the centrifugal
equator.
). A given
point P of the magnetosphere is defined by
two coordinates: (i) the dipole equatorial radius L of its own magnetic field line and
(ii) its centrifugal latitude, that is the angle between OP and the centrifugal
equator.
In construction of a 2-D model of the spatial distribution of a
plasma with N particle species we need to determine the properties
at each point ![]() (described by its value of the curvilinear
co-ordinate along the magnetic field) using a system of N+1 equations
(the equations of density (10) plus charge neutrality) with N+1
unknowns (the densities and the ambipolar electric potential
(described by its value of the curvilinear
co-ordinate along the magnetic field) using a system of N+1 equations
(the equations of density (10) plus charge neutrality) with N+1
unknowns (the densities and the ambipolar electric potential ![]() at point
at point ![]() ).
).
Solving the set of equations using Newton's method, we pose
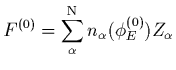 |
(15) |
| (16) |
 |
Finally, note that the kappa thermal speeds
![]() (needed for solving equation 10) are
derived from the parallel and perpendicular temperatures of the core
and halo components of the ions
(needed for solving equation 10) are
derived from the parallel and perpendicular temperatures of the core
and halo components of the ions
![]() , using
, using
